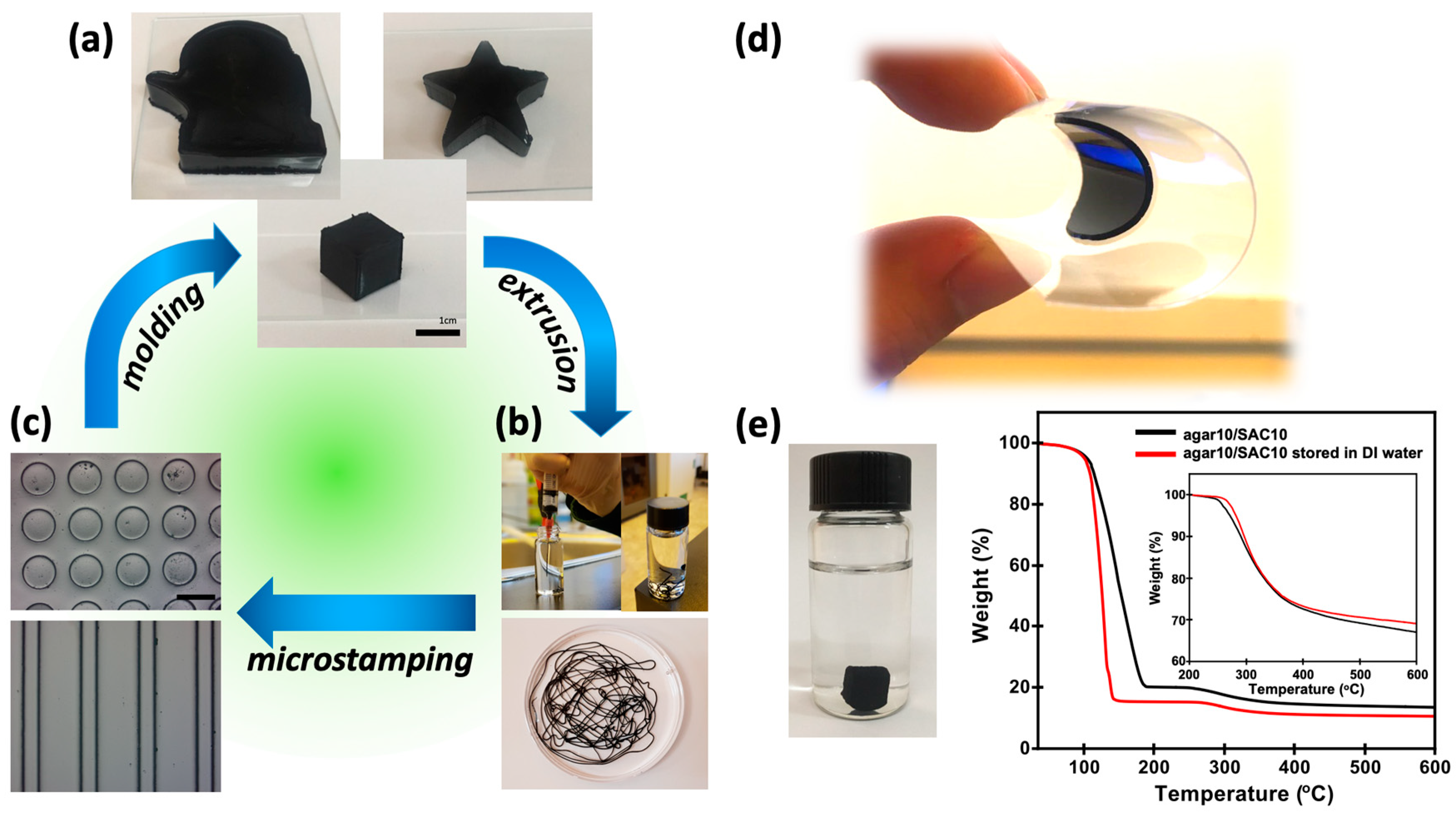
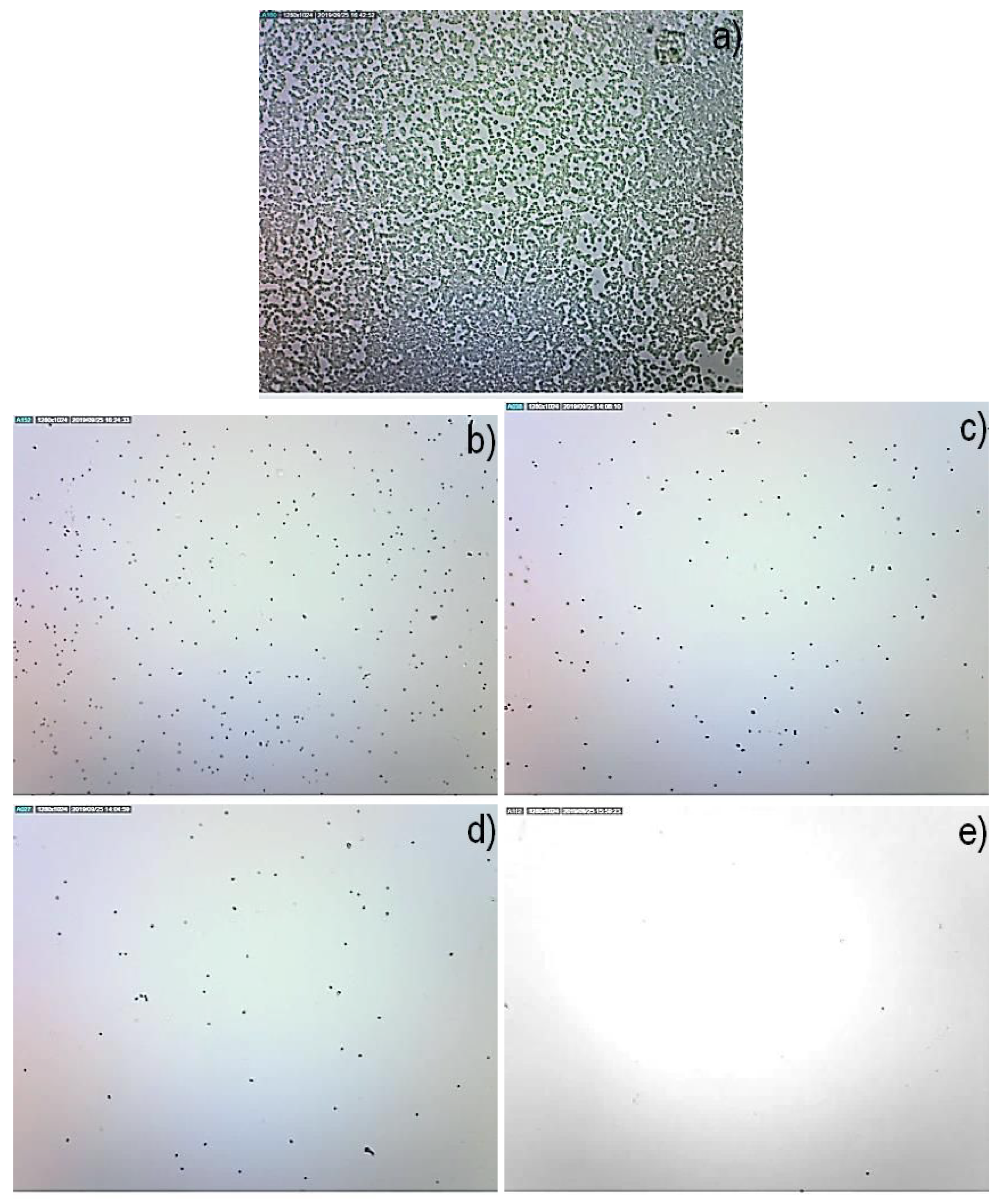
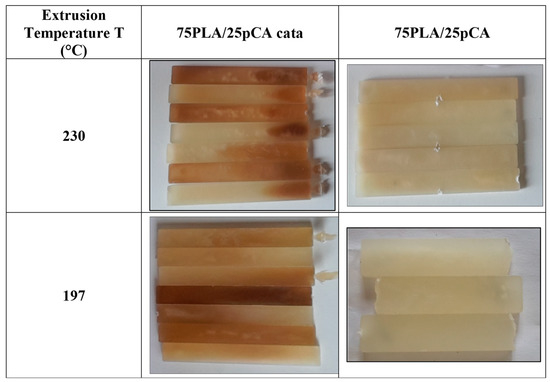
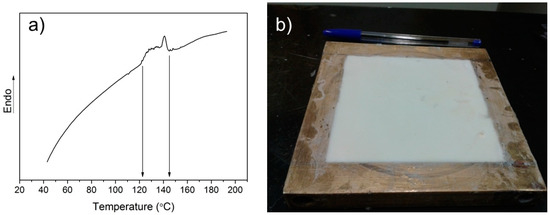
Floor Temperature Polymerization

Generally the ceiling temperature of a given polymer is correlated to the steric hindrance of the polymer s monomers.
Floor temperature polymerization. This effect is the precise opposite of the ceiling temperature phenomenon as a result of the fact that the polymerization is both endoentropic and endothermic δ h ls 13 3 kj mol 1 where the subscripts denote liquid monomer l going to a solution of. Is the temperature at which propagation and depropagation are equal. Tsg has found that inconsistent polymerization can often be a result of inconsistent lamp temperature. Geelen mers the freezing.
Yet amid all benefits of epoxy resins there is the unavoidable fact that epoxy isn t easy to work with. When the temperature increases to 60 degrees celsius epoxy reaches the heat distortion temperature hdt and it begins to deform. Dainton s equation states that at the equilibrium point i e when δg p 0 there is a critical temperature referred to as the ceiling temperature t c or floor temperature t f depending on the thermodynamic features of the polymerization. Pvc is the world s third most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer after polyethylene and polypropylene about 40 million tons of pvc are produced each year.
Thus it is not crystallization but a sufficient decrease of temperature which makes polymerization possible. Is the temperature below which polymerization cannot occur. The strength of its bounding characteristics and the nice durable sheen it leaves as a coating and the flexibility it offers for varying applications make epoxy a truly amazing compound. Thus the net rate of polymer growth is zero.
Pvc comes in two basic forms. A complication may arise from the fact that upon cooling certain mono 591 d. The limiting temperature below which polymerization is possible is the well known ceiling temperature to see figure 1. Ceiling temperature is a measure of the tendency of a polymer to revert to its constituent monomers when a polymer is at its ceiling temperature the rate of polymerization and depolymerization of the polymer are equal.
This is the point when we can expect and experience a very stable energy output most often measured in mw cm2. Above the ceiling temperature depolymerization will occur and the polymer will revert to its monomer. All these block copolymers except for 51 were obtained in a very high blocking efficiency because of the living nature of the polymerization of each comonomer the block polymers 50 52 and 53 are amphiphilic among which 52 exhibits an excellent surface activity and reduces the surface tension of water to 30 dyn cm 1 3 10 2 n m 1 or below at room temperature. At this point no conversion of monomer to polymer is obtained.
As temperature increases a significant amount of the flexural and compressive strength of epoxy decreases. Once the exposure bed gets up to temperature typically the exhaust fans will start and keep the lamps at a consistent temperature. The floor temperature for the polymerization of molten s 8 is thus 159 c.