Floor Of Sella Turcica Bone
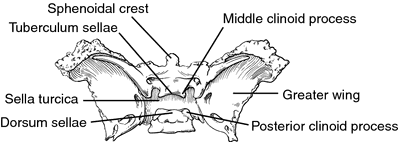
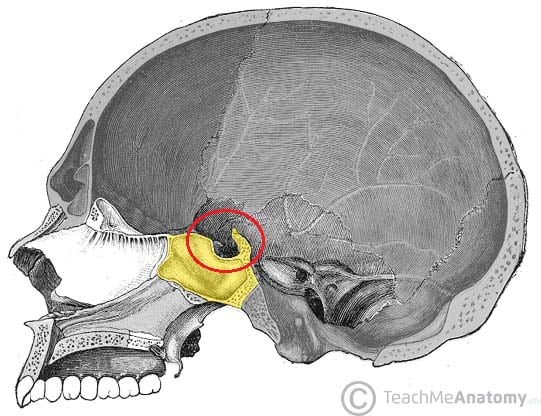
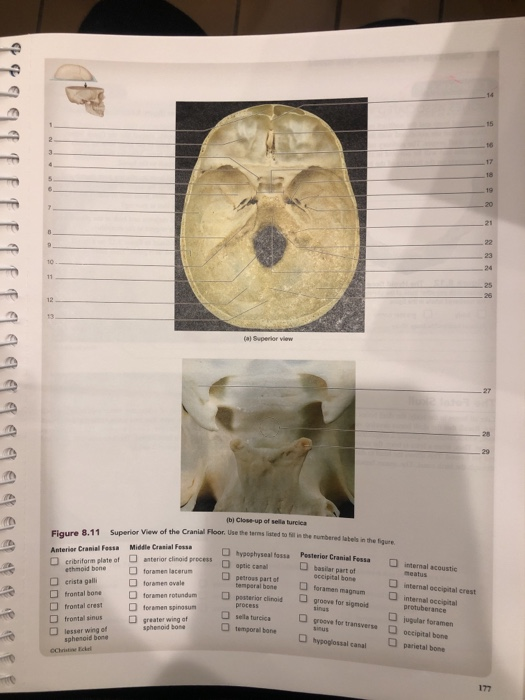
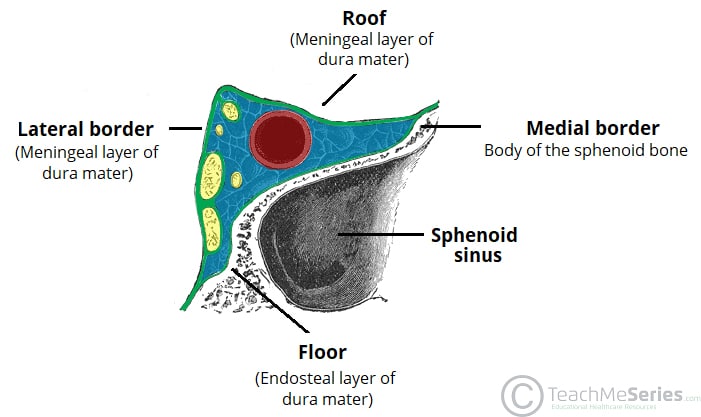
The sella turcica is a depression in the central region of the sphenoid bone.
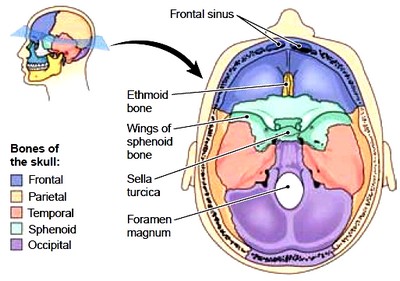
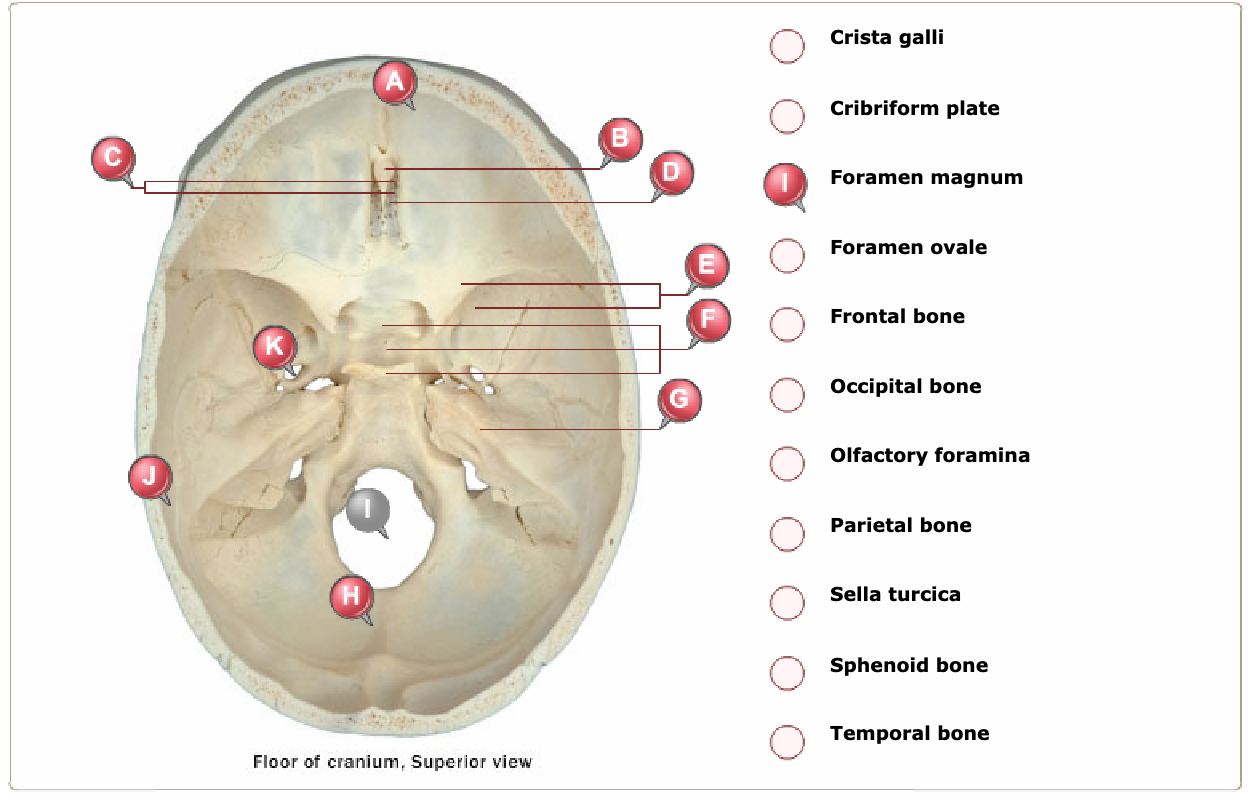
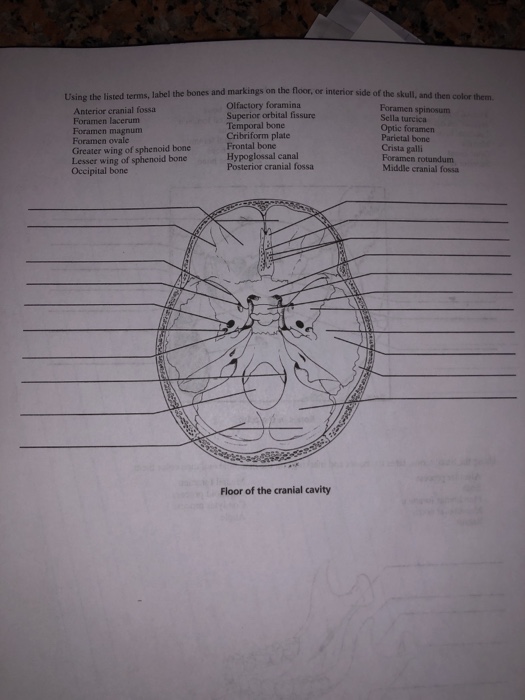
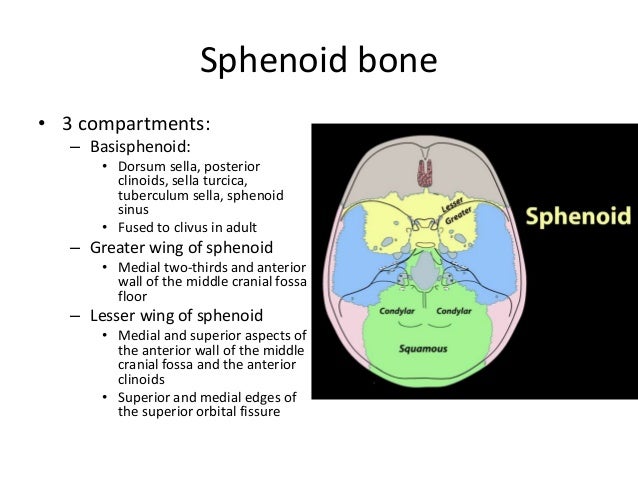
Floor of sella turcica bone. Two greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two lesser wings from the anterior side. The sella turcica latin for turkish seat is a saddle shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees orangutans and gorillas it serves as a cephalometric landmark the pituitary gland or hypophysis is located within the most inferior aspect of the sella turcica the hypophyseal fossa. Sella tur cica a depression on the upper surface of the sphenoid bone lodging the pituitary gland. Figure 1 2 saddle like depression which is sella turcica.
It is divided into three fragments and consists of an anterior wall a floor and a posterior wall. 2 not surprisingly many patients. Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides directed downwards from the junction of. The sphenoid bone.
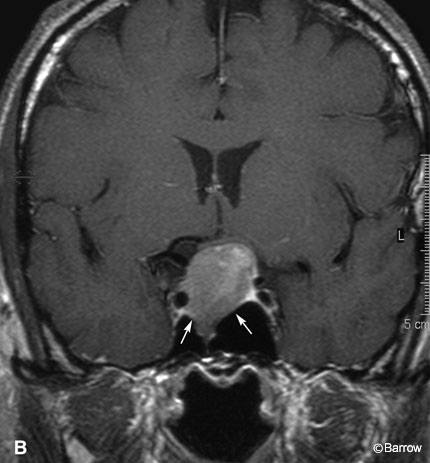
Empty sella see empty sella syndrome. The sphenoid bone sph forms the bony floor of the sella turcica. Which of the following bones do not contain a sinus. The sella turcica sella saddle.
The sella turcica is a cup shaped depression in the central basisphenoid bone which contains the pituitary gland and inferior part of the infundibular stalk. Miller keane encyclopedia and dictionary of medicine nursing and. It is divided into the following parts. The sella turcica is a spherical depression in the superior surface of the sphenoid bone.
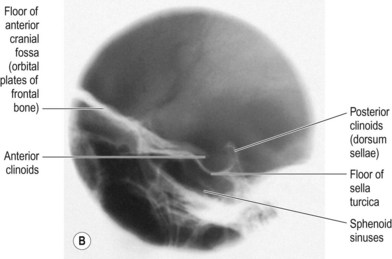
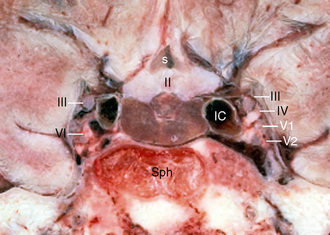
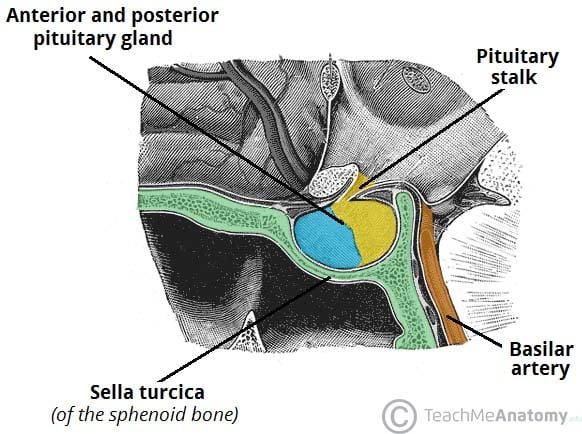
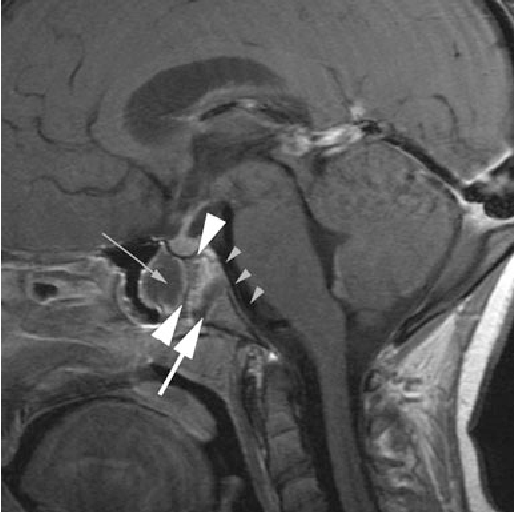
Coronal cryomicrotome section through the sella turcica. The empty sella turcica was first described in 1949 as a condition where the sella turcica is only partially filled by the pituitary gland which appears flattened against the sellar floor fig. The purplish pituitary gland unlabeled rests on the floor of the sella between the paired cavernous segments of the internal carotid arteries ic. Figure 14 4 gross anatomy of the sella and pituitary gland.
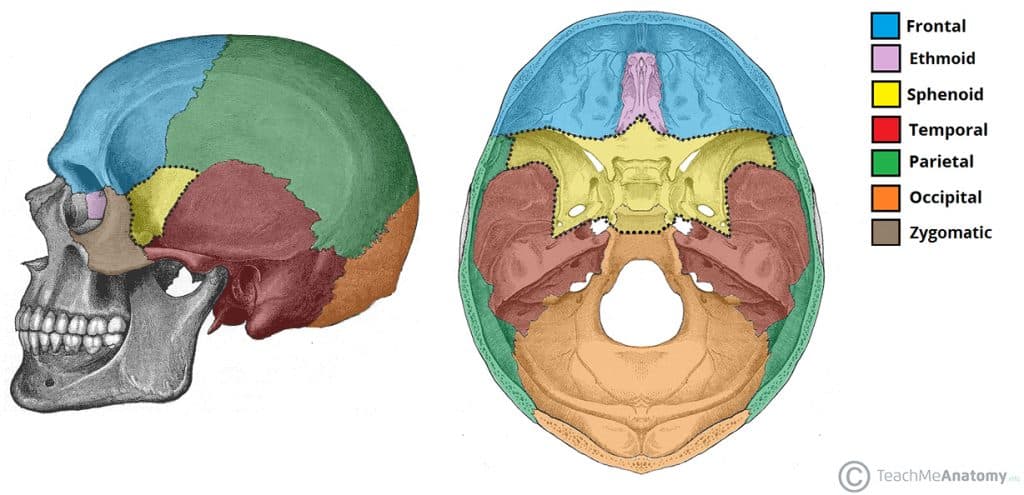
Sella sel ah l a saddle shaped depression. The sellar floor is continuous anteriorly with the tuberculum sellae and posteriorly with the dor sum sellae. Anatomically the sella turcica has been expressed as variable. A median portion known as the body of sphenoid bone containing the sella turcica which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses the sphenoidal sinuses.
Sella turcica resembles as saddle like depression which provide place for the pituitary gland. The sphenoid bone contains two cavities known as the sphenoidal sinuses. Sella turcica in the superior aspect of the sphenoid bone. 1 autopsy studies confirm the high disease prevalence reported to be 5 5 to 20 of the general population.
It houses the pituitary gland. The anterior part of the sella turcica which forms the horn of the saddle is a ridge called the tuberculum sellae.