Floor Of Carotid Triangle

Posterior belly of digastric m.
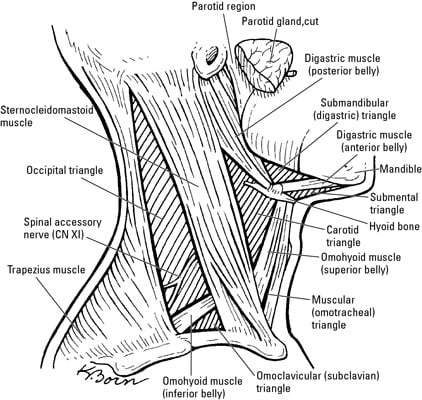
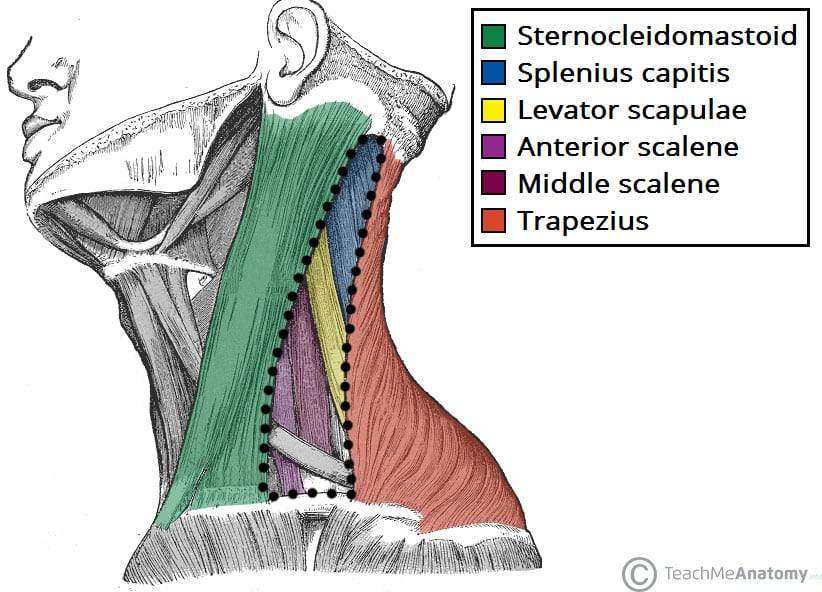
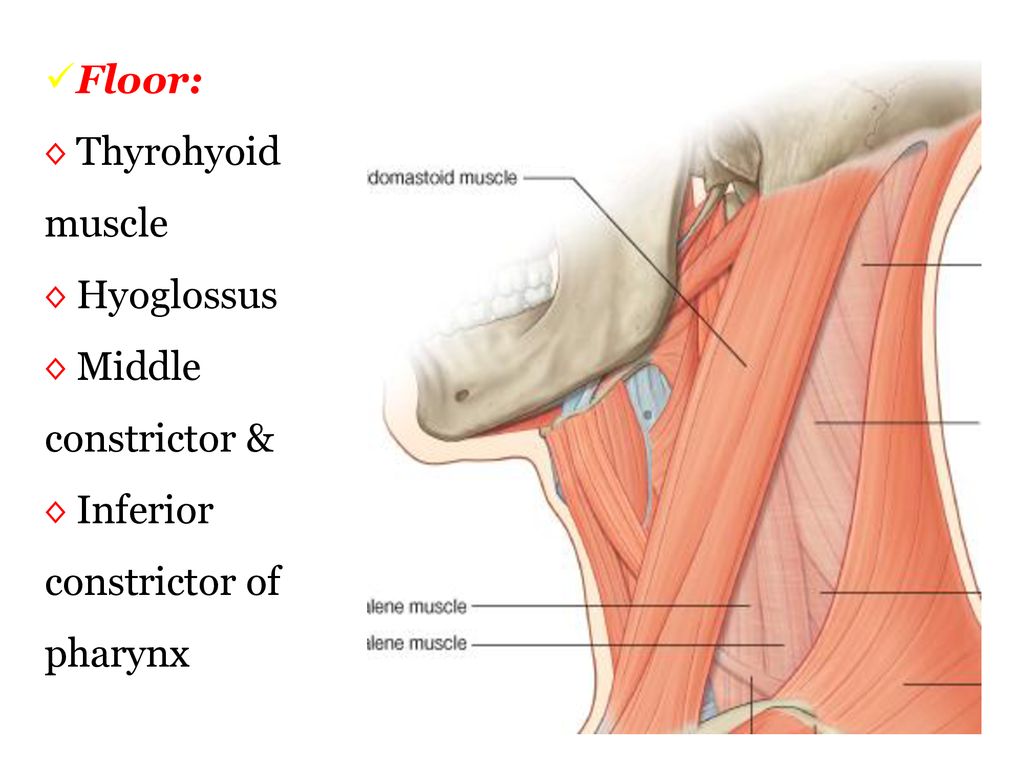
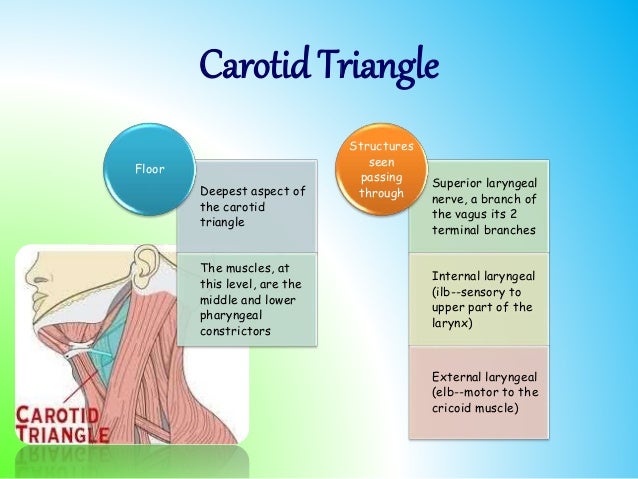
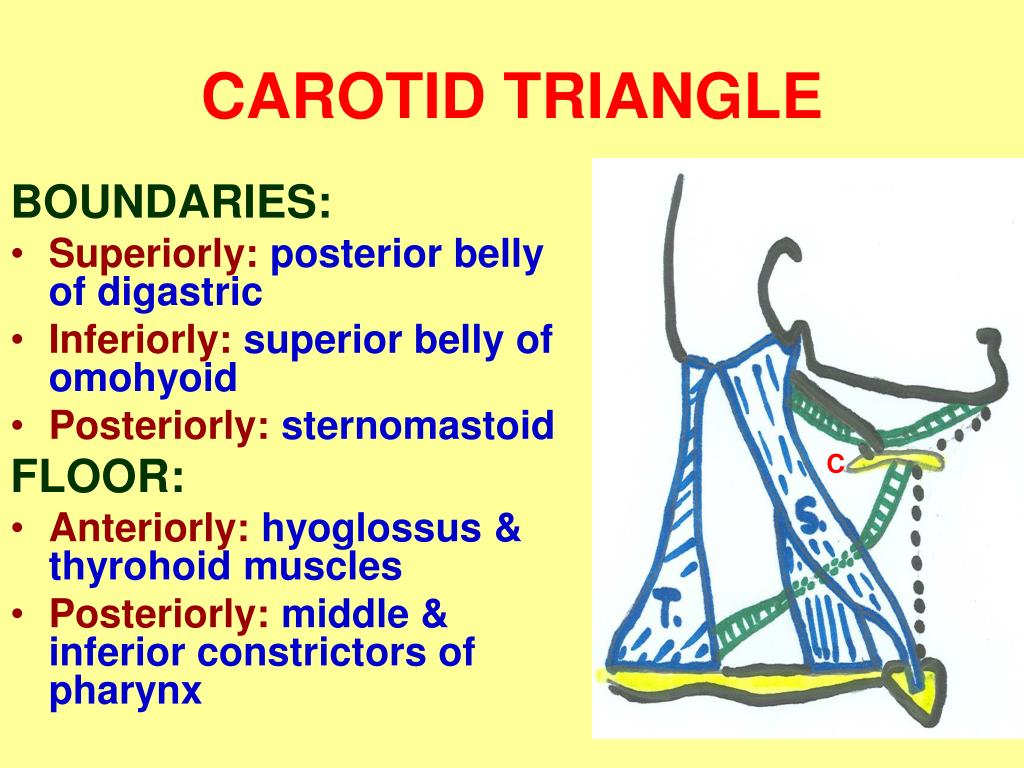
Floor of carotid triangle. Content edit edit source. However it is the posterior margin of the superior omohyoid muscle that limits the triangle anteriorly and the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid posteriorly. Its floor is formed by parts of the thyrohyoid membrane hyoglossus and the. Medially the floor of the triangle is formed by parts of the thyrohyoid muscle the hyoglossus muscle and the middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles.
Similar to the muscular triangle the carotid triangle has the omohyoid and sternocleidomastoid muscles as parts of its borders. Floor of carotid triangle dr. Floor of digastric triangle is formed by mylohyoid anteriorly hyoglossus posteriorly infrahyoid ribbon muscles are the chief contents of muscular triangle. It is so called because it contains all the 3 carotid arteries viz.
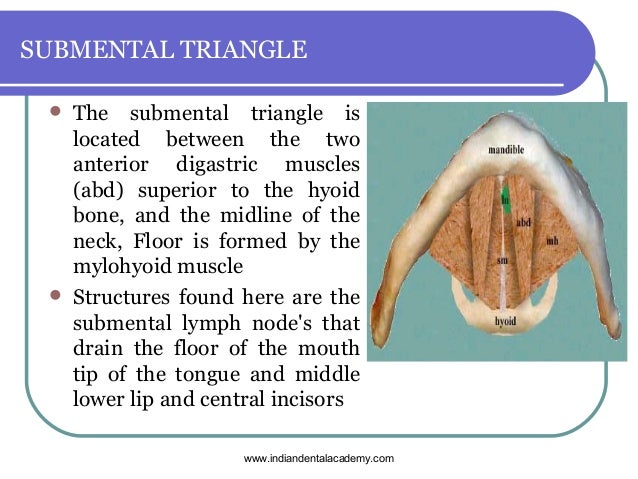
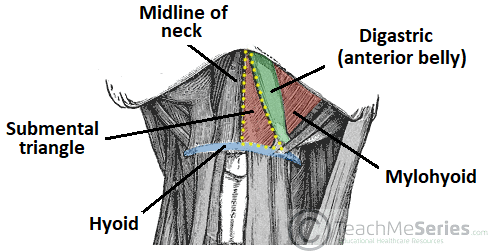
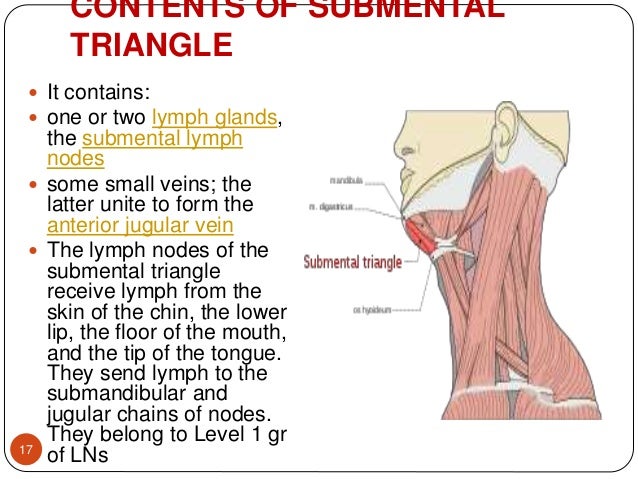
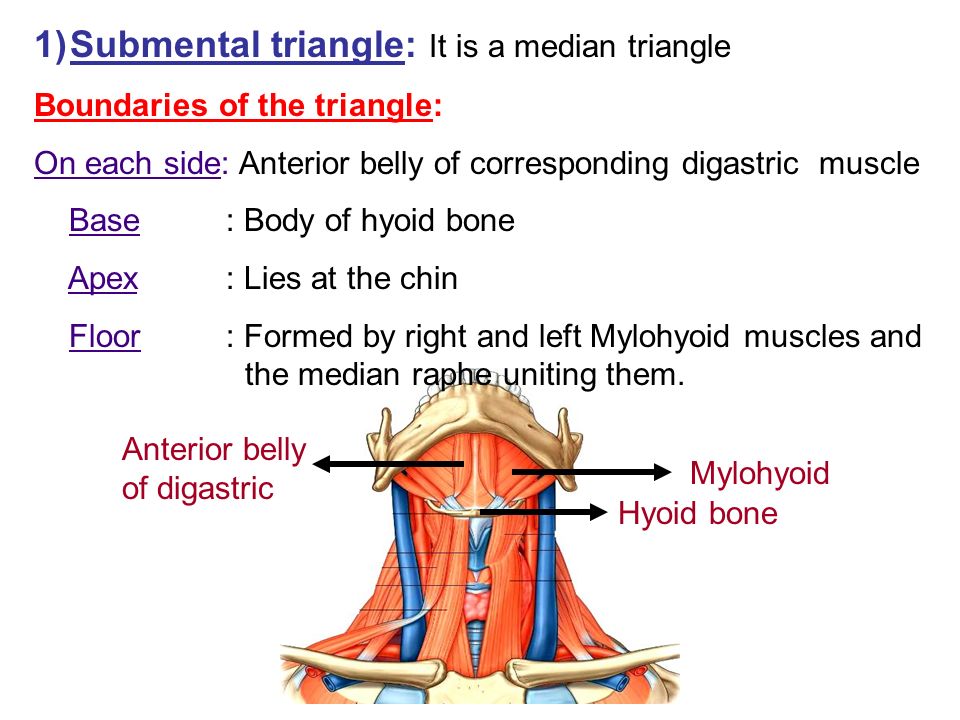
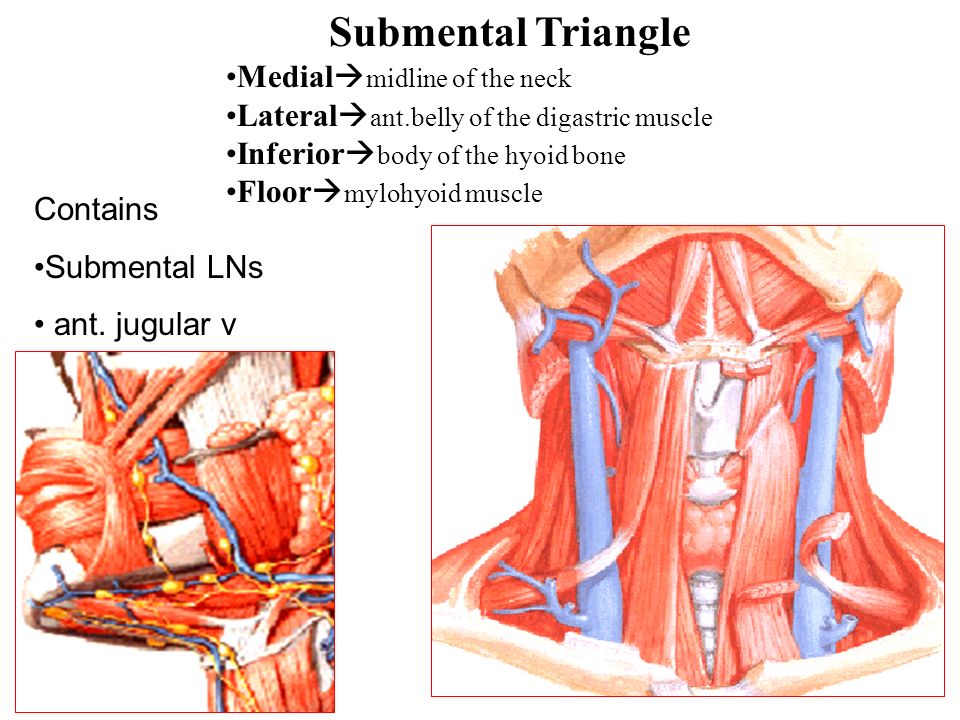
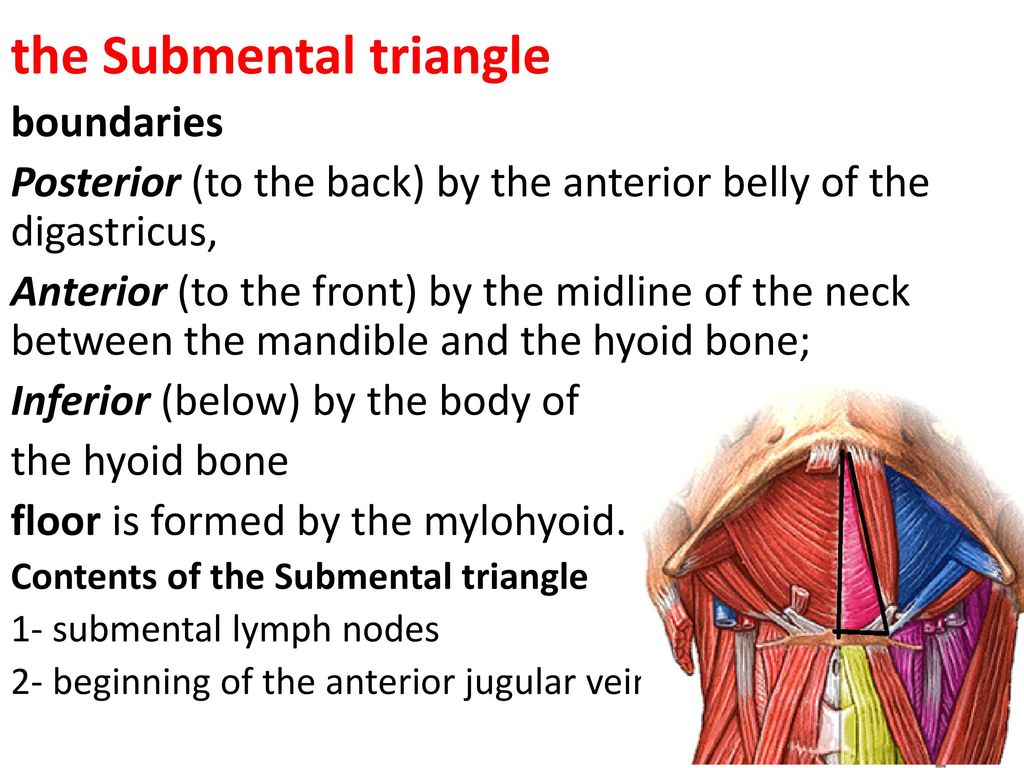
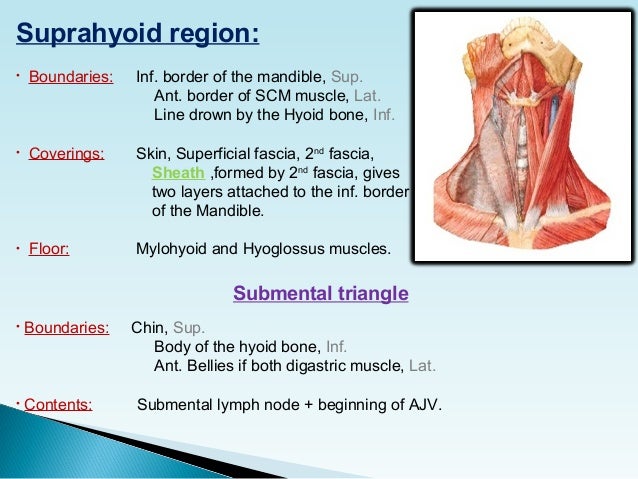
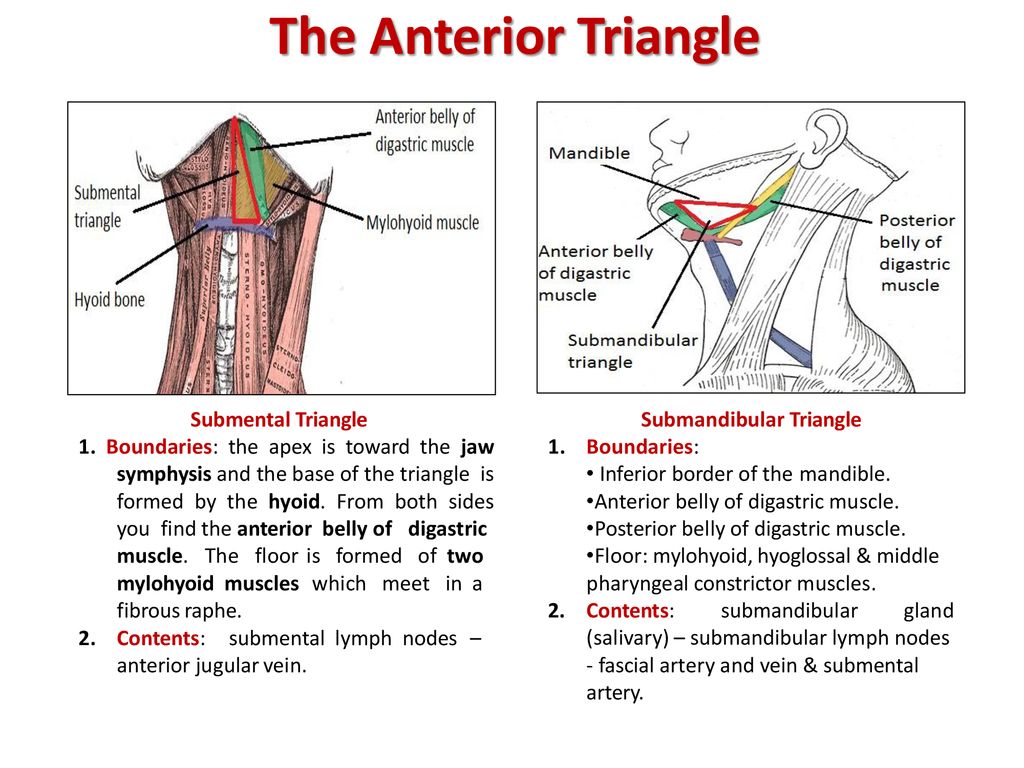
Hyoid bone thyro hyoid m. Inferiorly hyoid bone. Hyoglossus and thyrohyoid muscles posterior part. It contains the submental lymph nodes which filter lymph draining from the floor of the mouth and parts of the tongue.
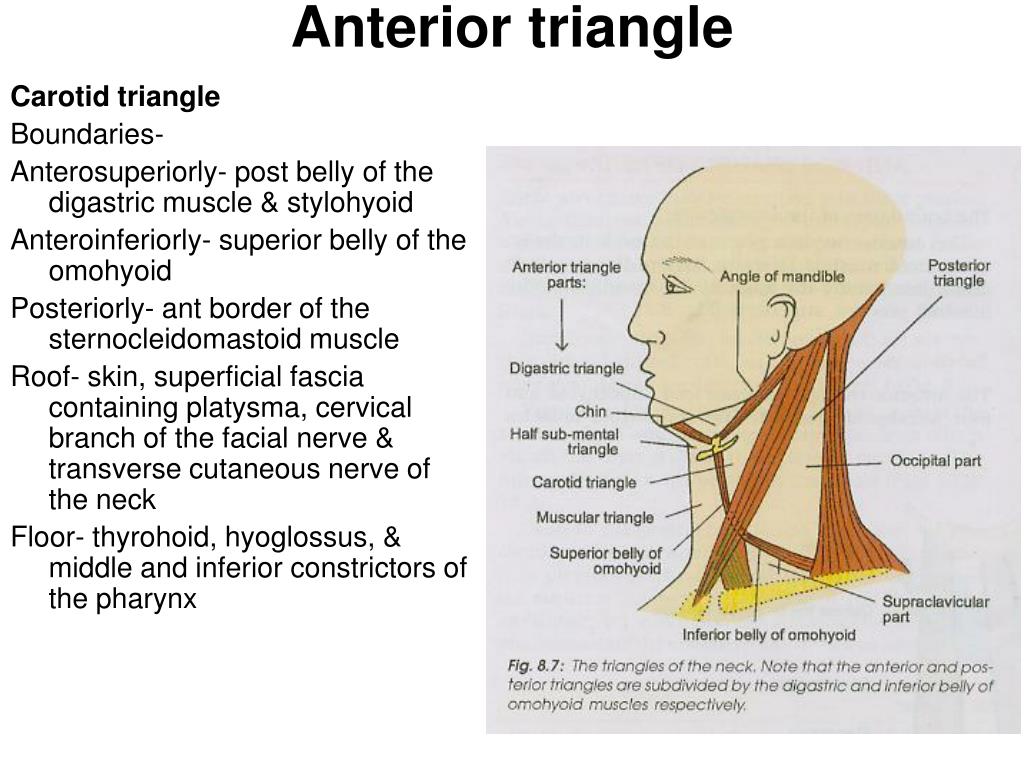
The carotid triangle or superior carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck coverings and boundaries. Posteriorly by the anterior. What is the clinical significance of enlargement of the jugulo digastric and jugulo omohyoid. Carotid triangle is one of the subdivisions of anterior triangle of neck.
The carotid triangle also contains the carotid sinus a dilated portion of the common carotid and internal carotid arteries. Constrictores pharyngis medius and inferior. It is bound by the sternocleidomastoid muscle by the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle and by the posterior belly of the digastric muscle with the stylohyoideus. Common carotid internal carotid and external carotid its boundaries are.
The hyoid bone can be seen in the most anterior angle of the carotid triangle with two of the three sides either originating or inserting upon it. This triangle is situated between the ophthalmic and maxillary divisions of the trigeminal nerve and the bone of the middle fossa between the foramen rotundum and superior orbital fissure figs. Middle constrictor and inferior constrictor muscles. Superior belly of omohyoid m.
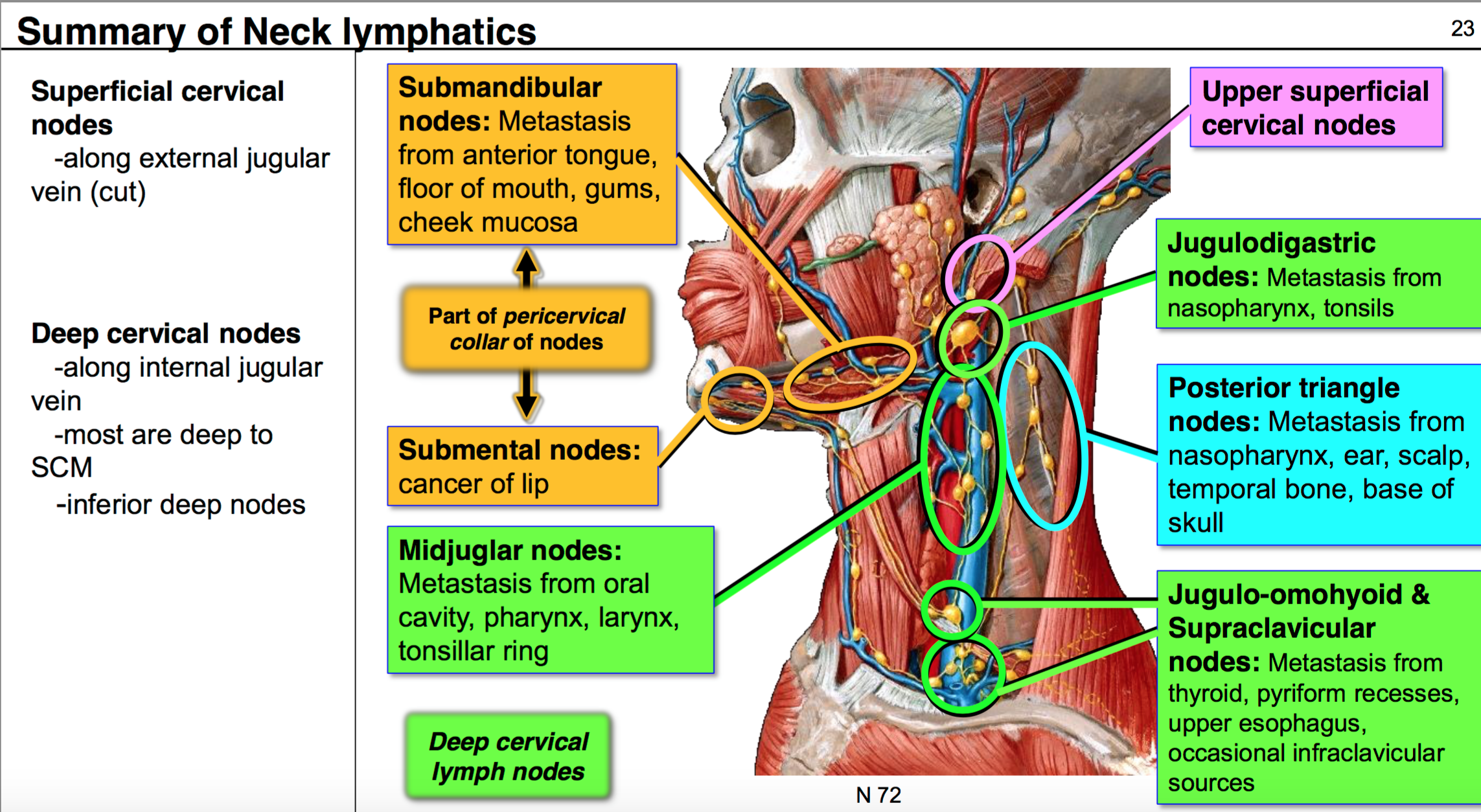
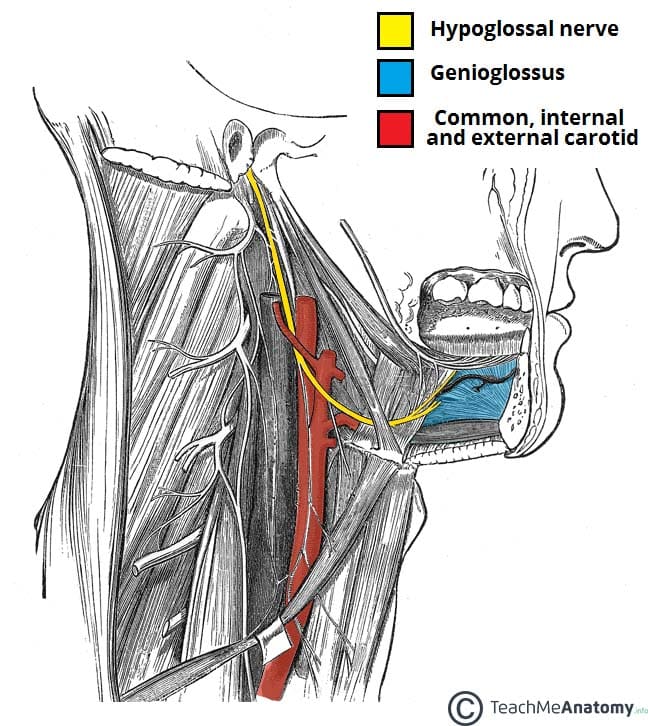
Hypoglossal nerve is a content of both digastric carotid triangles. Posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid. Structure superficial to mylohyoid in anterior digastric triangle is mylohyoid artery nerve. Describe the locations of the superficial and deep cervical lymph nodes.
Name the structures forming the boundaries of carotid triangle. Superior belly of omohyoid. This space is used to expose the superior orbital vein and the sixth cranial nerve and to access carotid cavernous fistulae.

:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3982/e7edZa4izRPlbDSqDu4qA_digastric_muscle_posterior_belly.png)














:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12695/triangles-of-the-neck_english.jpg)









:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12542/Neck_viscera_anterior_view.png)