Floor Insulation U Values Building Regulations

Recent changes to the building regulations have reduced the stipulated u value for.
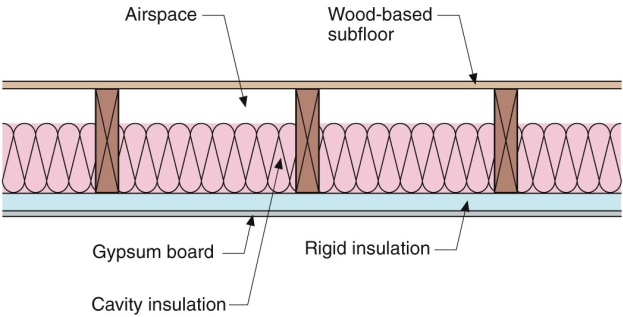
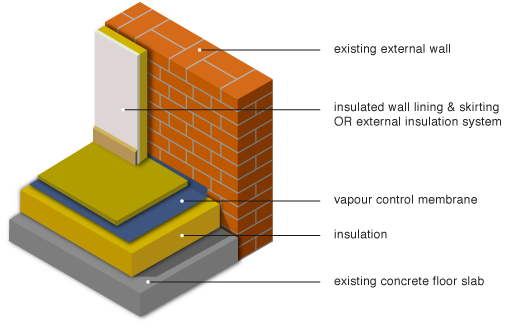
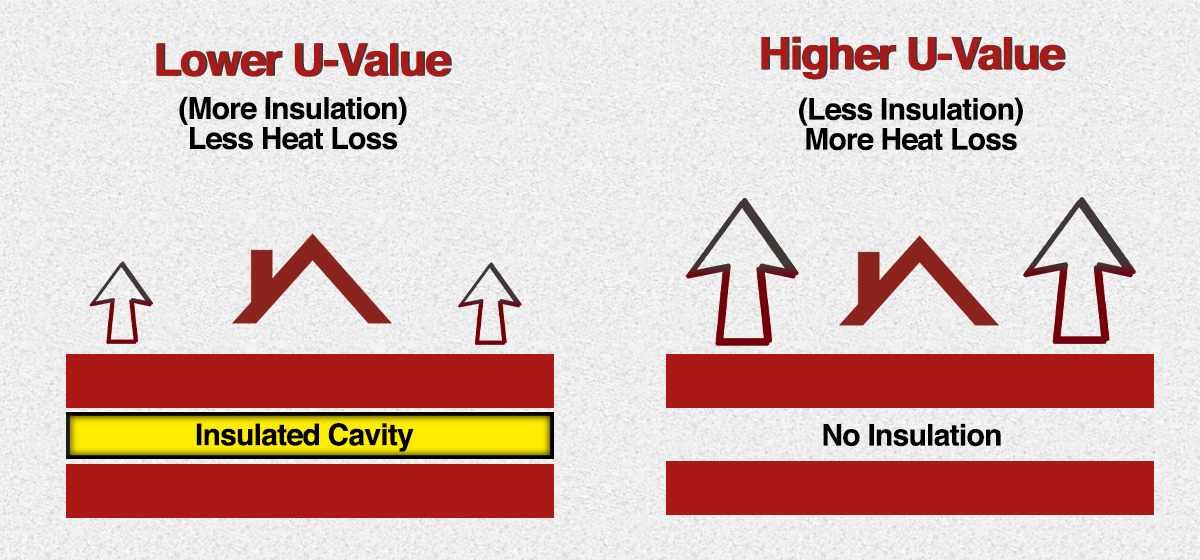
Floor insulation u values building regulations. U value requirements the u value of a building element i e walls floors or roofs is a measure of the thermal efficiency or heat loss through that element the lower the u value the better the thermeal efficiency of the element. This means that the higher the u value the worse the thermal performance of the building envelope. In 1976 as a result of the 1973 oil crisis building regulations reduced the required u value down to 1 but it remained 1 7 for semi exposed walls. The building regulations require that floors achieve minimum thermal performance values u values a measure of how quickly heat will travel through the floor and this affects the amount of insulation required.
The limiting u value the maximum u value that cannot be exceeded required under current building regulations are. U values building regulations and insulation a rough guide to understanding. If you compare this with a passivhaus designed house air leakage is an order of magnitude lower at below 0 6m hr per m. A u value is a measure of heat loss in a building element such as a roof wall or floor.
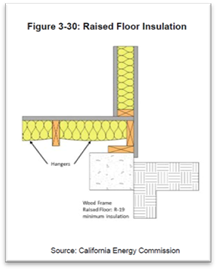
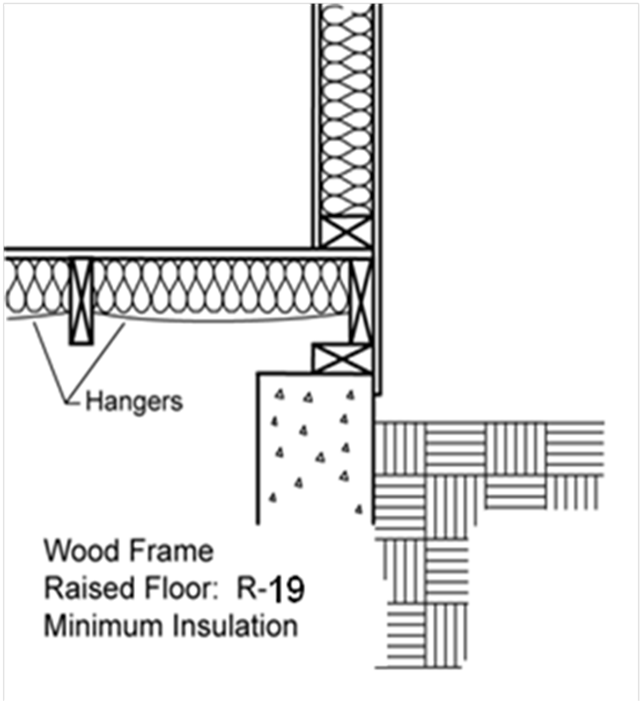
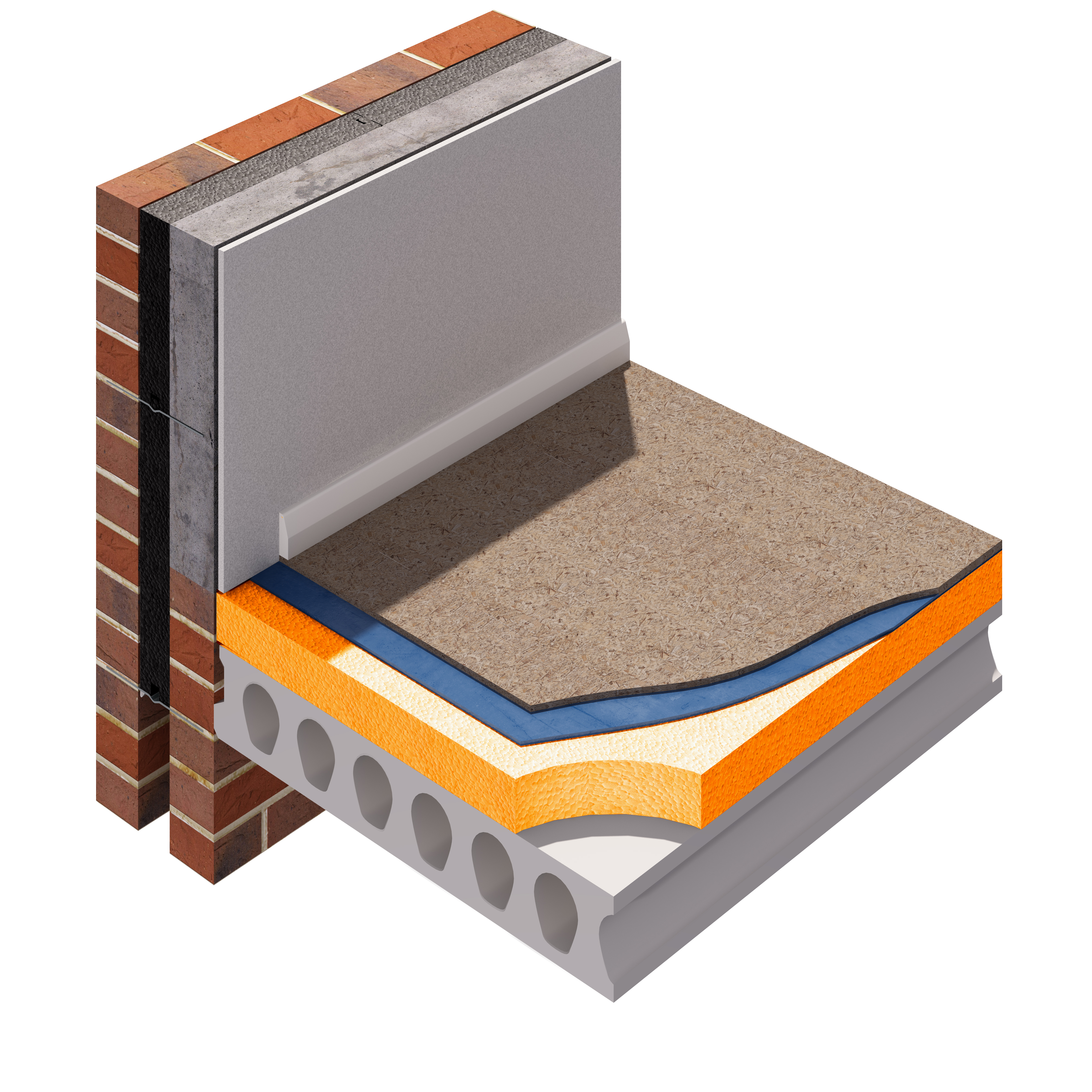
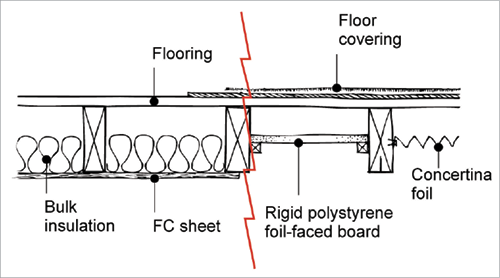
The importance of insulating floors. In 1985 the required u value dropped to 0 6 for walls hence many properties began to be insulated this is about the time we begin to see cavity wall insulation installed as standard. The installation of insulation in your floor must meet the minimum energy efficiency values set out in the approved documents. The ip 3 90.
Ireland s building regulations specifically part l conservation of fuel and energy dwellings 2011 technical guidance document outline the required u value for each area of a home. The u value requirments for building elements are outlined in part l. The lower the u value the less heat will be lost through a building element like an external wall or the foundation of a house. U values and building regulations.
It can also be referred to as an overall heat transfer co efficient and measures how well parts of a building transfer heat. Heat rises as denser colder air falls and pushes the warmer air up and is more likely to escape through the roof. Of the building regulations 2007. U values measure the effectiveness of insulating materials.